In the dynamic and diverse landscape of the modern workplace, the pursuit of fair hiring practices stands as a crucial imperative. Beyond merely ticking compliance boxes, organizations are increasingly recognizing the importance of cultivating an inclusive environment that values diversity at every level. As a senior professional content creator, this comprehensive exploration delves into the nuances of fair hiring practices, with a specific focus on unveiling and overcoming unconscious bias. Anchored in the principles of Sustainable HR Practices, we will navigate through key subheadings, dissecting their significance and providing insights into fostering a hiring process that is not only legally sound but also genuinely equitable.
What are Fair Hiring Practices?
Fair hiring practices encapsulate a set of ethical and unbiased procedures aimed at ensuring that all candidates are given an equal opportunity in the recruitment process. These practices go beyond legal requirements to foster diversity, equity, and inclusion within the workforce. Fair hiring involves creating a level playing field where individuals from varied backgrounds, regardless of race, gender, age, or other characteristics, have an equal chance to showcase their skills and contribute to the organization.
Understanding Unconscious Bias
Unconscious bias refers to the subtle and unintentional prejudices that can influence decision-making processes. In the context of hiring, these biases may manifest in various forms, such as affinity bias, confirmation bias, or the halo effect. To foster fair hiring practices, it is essential to understand and acknowledge the existence of unconscious bias.
Impact of Unconscious Bias on Hiring
The impact of unconscious bias on hiring can be profound and insidious. This subheading explores how biases can affect candidate selection, perpetuate stereotypes, and contribute to a lack of diversity within the organization. It sheds light on the unintended consequences of biases that hinder the ability to tap into a diverse talent pool.
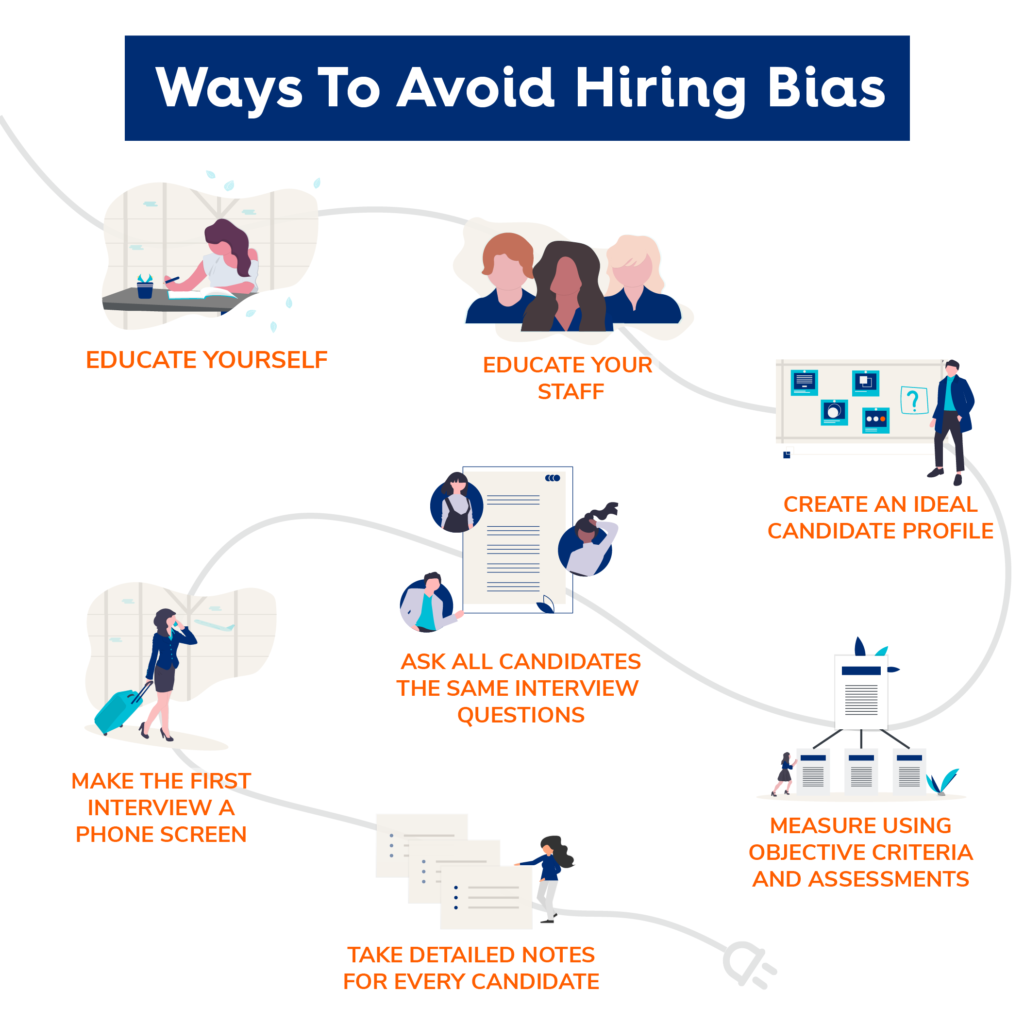
Strategies for Overcoming Unconscious Bias
- Blind Recruitment Processes
Blind recruitment involves removing identifiable information from resumes and applications, such as names, gender, or age, during the initial stages of the hiring process. This subheading delves into the advantages of blind recruitment in mitigating unconscious biases, allowing hiring decisions to be based solely on skills and qualifications.
- Diverse Interview Panels
Creating interview panels that represent diverse perspectives is a strategic move to counteract bias. This section discusses the benefits of having a diverse group of interviewers and how it contributes to fair hiring practices. It emphasizes the importance of including individuals with varied backgrounds and experiences in the decision-making process.
- Structured Interview Processes
Structured interviews involve asking all candidates the same set of questions, using predetermined criteria for evaluation. This subheading explores the advantages of structured interviews in minimizing subjective judgments and ensuring that each candidate is assessed based on the same criteria, promoting fairness in the evaluation process.
- Diversity Training for Hiring Teams
Providing diversity training for hiring teams is essential in raising awareness about unconscious biases. This section discusses the impact of training programs on creating a more inclusive mindset among hiring professionals. It explores the role of education in fostering an understanding of different perspectives and challenging stereotypes.
Pros and Cons of Fair Hiring Practices
Pros:
- Diverse Workforce
Fair hiring practices contribute to a more diverse workforce, bringing together individuals with varied perspectives and experiences.
Diverse teams are known to be more innovative, creative, and better equipped to solve complex problems.
- Enhanced Company Reputation
Organizations that prioritize fair hiring practices are likely to build a positive reputation as socially responsible employers.
A positive company image can attract top talent and improve relationships with customers and stakeholders.
- Higher Employee Morale
Employees feel more valued and engaged when they perceive that the organization is committed to fairness and equity.
Higher morale contributes to increased productivity, retention rates, and overall job satisfaction.
Cons
- Implementation Challenges
Implementing fair hiring practices may face resistance from existing organizational cultures or individuals accustomed to traditional hiring methods.
Adapting to new processes and criteria may require time and resources.
- Perceived Trade-offs with Qualifications
Some may perceive that a focus on diversity may compromise qualifications or merit-based hiring.
Balancing diversity goals with the need for specific skills and experience can be challenging.
- Potential for Tokenism
There’s a risk of organizations engaging in tokenism, where diversity is pursued for appearance rather than a genuine commitment to inclusivity.
Tokenism can undermine the effectiveness of fair hiring practices and create a false sense of diversity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fair hiring practices represent a commitment to building a workplace that values every individual, irrespective of their background. Unveiling and overcoming unconscious bias is a journey towards creating a more inclusive and equitable recruitment process. By embracing Sustainable HR Practices and incorporating strategies to address unconscious bias, organizations not only fulfil ethical and legal obligations but also position themselves as leaders in fostering a workplace where diversity thrives. As the business landscape continues to evolve, the genuine pursuit of fair hiring practices is not just a choice; it’s a strategic imperative that drives organizational success and societal progress.
Blog Writer:
Kriti Sharma
Young HR Talent Reformer , badgefree