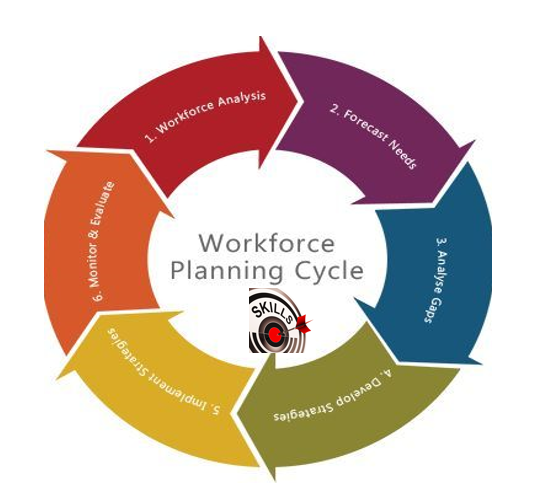
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations face constant challenges to stay competitive and adapt to ever-changing market dynamics. In this pursuit of growth and resilience, it is essential for organizations to focus on building a workforce that is skill-centric. A skill-focused approach to workforce planning can transform how organizations operate, cultivate talent, and achieve sustainable success. In this blog, we will explore the significance of skill-based workforce planning, the internal mapping done in organizations, the concept of talent supply-chain, and the importance of maintaining skill directories.
Internal Mapping: Understanding Your Workforce
Before an organization can adopt a skill-focused approach, it must conduct an internal mapping of its existing workforce. This process involves identifying and documenting the skills possessed by each employee, their proficiency levels, and the areas they excel in. By doing so, organizations can gain valuable insights into their talent pool, allowing them to make informed decisions when it comes to talent deployment and allocation.
The internal mapping process helps organizations identify skill gaps within the workforce. These gaps represent the skills that are lacking or in short supply among employees. Recognizing these gaps is critical to developing targeted training and development programs to upskill employees and fill those gaps effectively.
So, basically internal skill mapping in an organization is a crucial process that involves identifying, assessing, and cataloguing the skills possessed by employees across different levels and departments. Here are some key facts about internal skill mapping:
Skill Identification: Skill mapping starts with identifying the various skills that employees possess. These skills can range from technical competencies to soft skills like communication, leadership, and problem-solving.
Comprehensive Assessment: The process of skill mapping involves conducting a comprehensive assessment of each employee’s skills. This can be done through self-assessments, manager assessments, or skill assessment tests.
Skill Proficiency Levels: Skill mapping not only identifies the skills but also assesses the proficiency levels of each employee in those skills. This helps in understanding the depth of expertise within the organization.
Skill Gaps: One of the primary purposes of skill mapping is to identify skill gaps within the organization. These gaps represent areas where employees lack proficiency or where critical skills are in short supply.
Training and Development: Skill mapping results in the identification of training and development needs for employees. It helps in designing targeted training programs to upskill employees and fill the identified skill gaps.
Succession Planning: Skill mapping plays a vital role in succession planning. By understanding the skills of employees, organizations can identify potential successors for key roles and proactively groom them for future leadership positions.
Resource Allocation: Knowing the skills of each employee enables efficient resource allocation. When projects or tasks require specific skills, managers can easily identify and assign the right individuals to optimize project outcomes.
Performance Appraisal: Skill mapping data can be integrated into the performance appraisal process. It provides a more holistic view of an employee’s performance by considering not only their job-specific tasks but also their overall skill development.
Agile Workforce Planning: Skill mapping enables organizations to adapt quickly to changing business needs. By having a clear picture of their employees’ skills, they can respond promptly to new opportunities and challenges.
Career Development: Employees benefit from skill mapping as it provides insights into their own skill strengths and areas for improvement. This information can guide their career development and help them align their aspirations with the organization’s needs.
Workforce Diversity and Inclusion: Skill mapping helps identify and appreciate the diverse skills and talents that employees bring to the table. This promotes a culture of inclusion and recognizes the value of a varied skillset within the organization.
Continuous Improvement: Skill mapping is not a one-time process. It should be regularly updated to reflect changes in the organization and employees’ skill development. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement and learning.
Data-Driven Decision Making: Skill mapping provides valuable data for strategic decision-making. It helps HR and management make informed choices regarding talent development, succession planning, and resource allocation.
In summary, internal skill mapping is an essential tool for organizations to understand the capabilities of their workforce, optimize talent deployment, and enhance overall performance and productivity. By investing in skill mapping, organizations can build a skilled, adaptable, and competitive workforce to thrive in today’s ever-changing business environment.
Talent Supply-Chain: Sourcing and Nurturing Skills
In skill-focused workforce planning, talent is seen as a dynamic supply-chain rather than a static resource. Talent supply-chain involves the process of continuously sourcing and nurturing skills to align with organizational objectives. Traditional workforce planning often revolves around hiring individuals for specific roles. However, a skill-focused approach emphasizes the importance of nurturing and developing existing talent, rather than solely relying on external recruitment.
Talent supply-chain management includes activities such as:
Internal Mobility: Encouraging employees to explore diverse roles within the organization helps develop a versatile workforce. Internal mobility not only enhances employees’ skillsets but also boosts engagement and reduces turnover.
Upskilling and Reskilling: Organizations should invest in training and development programs to upskill employees in areas where they may lack proficiency. Additionally, reskilling helps employees adapt to technological advancements and new job requirements.
Knowledge Sharing: Encouraging knowledge sharing and peer learning within the organization creates a culture of continuous learning, fostering a skilled and collaborative workforce.
Talent Acquisition Strategies: When hiring externally, organizations should focus on identifying candidates with the right skills, as well as the potential for growth and adaptability. This ensures a constant inflow of talent that aligns with the organization’s skill requirements.
Maintaining Skill Directories: A Blueprint for Success
Skill directories serve as blueprints for an organization’s skill-focused workforce planning efforts. These directories centralize information about employee skills, qualifications, and experiences. With a skill directory in place, organizations can easily identify the skills available within their workforce and streamline decision-making processes.
A well-maintained skill directory offers several advantages:
Agility in Decision-Making: Skill directories provide real-time information about the organization’s skill capabilities, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making. This agility is essential for responding to market shifts and adapting to new challenges promptly.
Targeted Skill Development: Skill directories allow HR and management to identify skill gaps and tailor training and development programs to address specific needs. This targeted approach leads to more efficient skill development initiatives.
Succession Planning: Knowing the skills possessed by each employee facilitates effective succession planning. Organizations can identify potential successors for critical roles and proactively groom them to take on higher responsibilities.
Resource Allocation: Skill directories aid in optimizing resource allocation by matching the right talent to the right projects. This ensures that projects are staffed with skilled individuals, leading to improved project outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a skill-focused approach to workforce planning is indispensable for organizations striving to remain relevant and competitive in a rapidly changing world. By conducting internal mapping, nurturing a talent supply-chain, and maintaining skill directories, organizations can create a dynamic workforce that adapts to emerging challenges and opportunities. This proactive approach to talent management fosters innovation, agility, and sustained success for organizations in the long run.
Incorporating a skill-focused workforce planning strategy is not a one-time event; it requires ongoing evaluation and refinement. Organizations must embrace a culture of continuous learning and skill development to unlock their full potential and stay ahead in the modern business landscape.
Blog Writer:
Dhivyashree J
Young Business growth accelerator, badgefree